co2 electron pair geometry|CO2 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry and Hybridization : Tuguegarao The electronic configuration of the Carbon atom in its ground state is 1s22s22p2, and that of an Oxygen atom is 1s22s2p4. When the electrons are in an excited state, they jump to other orbitals. In its excited state, the atom’s electronic configuration becomes . Tingnan ang higit pa This Pokémon was first revealed during a livestream of Pokémon Omega Ruby & Alpha Sapphire. Towards the end of the livestream, Junichi Masuda revealed this Mega Evolution. It is said that the reason that it is a Mega Evolution, and not a Primal Reversion, will be revealed in-story. It is also said to Mega Evolve in a way different to .
PH0 · Number of Lone Pairs and Bonding Pairs for CO2 (Carbon dioxide)
PH1 · Electron Geometry for CO2 (Carbon Dioxide)
PH2 · CO2 Molecular Geometry and Bond Angles (Carbon Dioxide)
PH3 · CO2 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Molar
PH4 · CO2 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry and Hybridization
PH5 · CO2 Lewis Structure, Hybridization, Molecular Geometry, and MO Diagr
PH6 · CO2 Lewis Structure, Hybridization, Molecular Geometry, and
PH7 · CO2 Lewis Structure,
PH8 · CO2 Geometry and Hybridization
PH9 · 5.2: Molecular Shape
PH10 · 10.3: VSEPR Geometry
Fairly OddParents: A New Wish is a sequel to the original Nickelodeon animated comedy series that sees the return of the eccentric Fairy Godparents, Cosmo, and Wanda. A young girl named Hazel moves to the city with her parents and feels out of place until she discovers her next-door neighbors are a pair of magical godparents looking to grant her .
co2 electron pair geometry*******The molecular Geometry of any compound is based on the arrangement of atoms, electron pairs, and bonds. Here in CO2, both Oxygen atoms form sigma bonds with the central carbon atom and complete their octet. As a result, there are no lone pairs of electrons, but bonding pairs of electrons also repel . Tingnan ang higit paOne needs to know the Lewis structure in order to understand the molecular geometry of any given molecule. This structure helps in knowing the arrangement . Tingnan ang higit paThe electronic configuration of the Carbon atom in its ground state is 1s22s22p2, and that of an Oxygen atom is 1s22s2p4. When the electrons are in an excited state, they jump to other orbitals. In its excited state, the atom’s electronic configuration becomes . Tingnan ang higit pa
In this video we look at the electron geometry for CO2 (Carbon Dioxide). Because the Carbon dioxide molecule has two electron domains (two oxygen atoms and no . Learn how to draw the lewis structure of CO2, the hybridization of carbon and oxygen atoms, the molecular geometry and electron geometry of CO2, and the molecular . CO2 has a total of 16 valence electrons (carbon has 4 and two oxygen have 12) which are structured as O=C=O. Both oxygen and carbon atoms need 8 electrons to complete octet in their outermost shells.
A quick explanation of the molecular geometry of CO2 including a description of the CO2 bond angles. We can see that there are only two atoms attached to the central Carbon .
Learn how to draw the Lewis structure of CO2, its molecular geometry, hybridization, polarity and resonance structures. Find out the number of lone pairs, formal charges and bond angles in CO2 molecule.
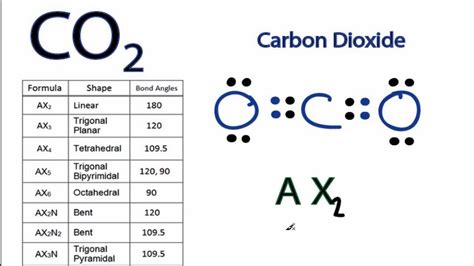
Sum the valence electrons from all the atoms. 3. Use a pair of electrons to form a bond between each pair of bound atoms. 4. Add the remaining electrons to satisfy the octet for a more electronegative atom first. 5. If any atoms lack an octet, .The premise of the VSEPR theory is that electron pairs located in bonds and lone pairs repel each other and will therefore adopt the geometry that places electron pairs as far apart from each other as possible.For example, the methane molecule, CH 4, which is the major component of natural gas, has four bonding pairs of electrons around the central carbon atom; the electron-pair geometry is tetrahedral, as is the molecular structure (Figure .
To determine the number of lone pairs and bonding pairs of electrons for CO2 we first need to draw as valid Lewis Structure. Once we have a Lewis Structure f. The electron geometry of CO2 is linear as well. Before you bombard me with questions about electron geometry, let me clear it out!! So molecular geometry is those which include only the atom while determining . The electron-pair geometry and molecular structure are identical, and CO 2 molecules are linear. (b) We write the Lewis structure of BCl 3 as: Thus we see that BCl 3 contains three bonds, and there are no lone pairs of electrons on boron. The arrangement of three regions of high electron density gives a trigonal planar electron-pair geometry. The electron geometry for CO2 is also linear. Since, the central Carbon (C) atom is surrounded by 2 regions of electron density, according to VSEPR theory, “the maximum distance two regions of electron density can .Carbon dioxide has two electron groups and no lone pairs. Carbon dioxide is therefore linear in electron-group geometry and in molecular geometry. The shape of CO 2 is linear because there are no lone pairs affecting the orientation of the molecule. Therefore, the linear orientation minimizes the repulsion forces.Electron-pair Geometry versus Molecular Structure. It is important to note that electron-pair geometry around a central atom is not the same thing as its molecular structure. The electron-pair geometries shown in Figure 7.16 describe all regions where electrons are located, bonds as well as lone pairs. Molecular structure describes the location of the atoms, not the electrons.Electron-Pair Geometry versus Molecular Structure. It is important to note that electron-pair geometry around a central atom is not the same thing as its molecular structure. The electron-pair geometries shown in Figure 7.2.3 describe all regions where electrons are located, bonds as well as lone pairs. Molecular structure describes the location of the atoms, not the electrons.Carbon dioxide has two electron groups and no lone pairs. Carbon dioxide is therefore linear in electron-group geometry and in molecular geometry. The shape of CO 2 is linear because there are no lone pairs affecting the orientation of the molecule. Therefore, the linear orientation minimizes the repulsion forces. A quick explanation of the molecular geometry of CO2 including a description of the CO2 bond angles.We can see that there are only two atoms attached to the .D With two nuclei around the central atom and one lone pair of electrons, the molecular geometry of SnCl 2 is bent, . The carbon in the –N=C=O fragment is doubly bonded to both nitrogen and oxygen, which in the VSEPR model gives carbon a total of two electron pairs. The N=C=O angle should therefore be 180°, or linear. The three fragments .co2 electron pair geometryD With two nuclei around the central atom and one lone pair of electrons, the molecular geometry of SnCl 2 is bent, . The carbon in the –N=C=O fragment is doubly bonded to both nitrogen and oxygen, which in the VSEPR model gives carbon a total of two electron pairs. The N=C=O angle should therefore be 180°, or linear. The three fragments . CO2 Molecular Geometry & Shape. In a CO2 molecule, the carbon atom is in the center double bonded with two oxygen atoms by each side. Both oxygen atoms have two lone pairs of nonbonding electrons present and .The concept of CO2 molecular geometry states that the molecular geometry of any compound depends on the arrangement of atoms, bonds, and electron pairs. While discussing CO2, both oxygen atoms make sigma bonds and the central carbon atom, and make their octet complete. Moreover, as an outcome, there are no lone pairs of electrons; however, the .
co2 electron pair geometry CO2 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry and Hybridization Table 1.1 Basic VSEPR Shapes. Notes: . For VSEPR purpose, the terms “shape” and “geometry” are interchangeable; “electron pair” and “electron group” are also interchangeable. Multiple bonds (double or triple .Predict the electron pair geometry (EPG) and molecular geometry (MG) of the following compounds based on the Lewis structure and VSEPR: A. H2O B. PF5 C. CO2 D. SO2 E. CHCl3 Predict the molecular geometry of the compound CO2 using VSEPR.

Electron-Pair Geometry versus Molecular Structure. It is important to note that electron-pair geometry around a central atom is not the same thing as its molecular structure. The electron-pair geometries shown in Figure 7.2.3 describe all regions where electrons are located, bonds as well as lone pairs. Molecular structure describes the location of the atoms, not the electrons.
Molecular Geometry of Carbon Diselenide (CSe2) From the Lewis structure of carbon diselenide, it is clear that this triatomic molecule has linear geometry. It is so because all the participating atoms are arranged in a straight line to form the bond angle of 180°. . It is this dipole cloud that is responsible to accept shared pair of . Electron-pair Geometry versus Molecular Structure. It is important to note that electron-pair geometry around a central atom is not the same thing as its molecular structure. The electron-pair geometries shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\) describe all regions where electrons are located, bonds as well as lone pairs.
VSEPR Theory. Valence shell electron-pair repulsion theory (VSEPR theory) enables us to predict the molecular structure, including approximate bond angles around a central atom, of a molecule from an examination of the number of bonds and lone electron pairs in its Lewis structure. The VSEPR model assumes that electron pairs in the valence shell of a central .
Andres Soriano Foundation offers assistance to patients with BREAST CANCER STAGE I-II or better. Patients must prepare the following: Profile of patient, diagnosis (original or certified true copy of medical abstract and histopathology or biopsy results), history, plan of treatment/doctor’s report with his name, signature and license number.
co2 electron pair geometry|CO2 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry and Hybridization